Every motorist is familiar with the situation when his car stops starting because of a battery malfunction. The ignorant driver in this case simply buys a new battery, and the old one, which has not served such a long time, throws it away or gives it to the scrap collection point. Is it worth it?
The reasons for the failure of the "heart" of the electrical equipment of the vehicle are many. Often, the main cause of the failure of the power source is the sulfation of the plates. This problem manifests itself vividly, because the engine does not start even when the battery is fully charged, and the included headlights discharge the battery in just a couple of three minutes.
Content
What is sulfation of the battery plates
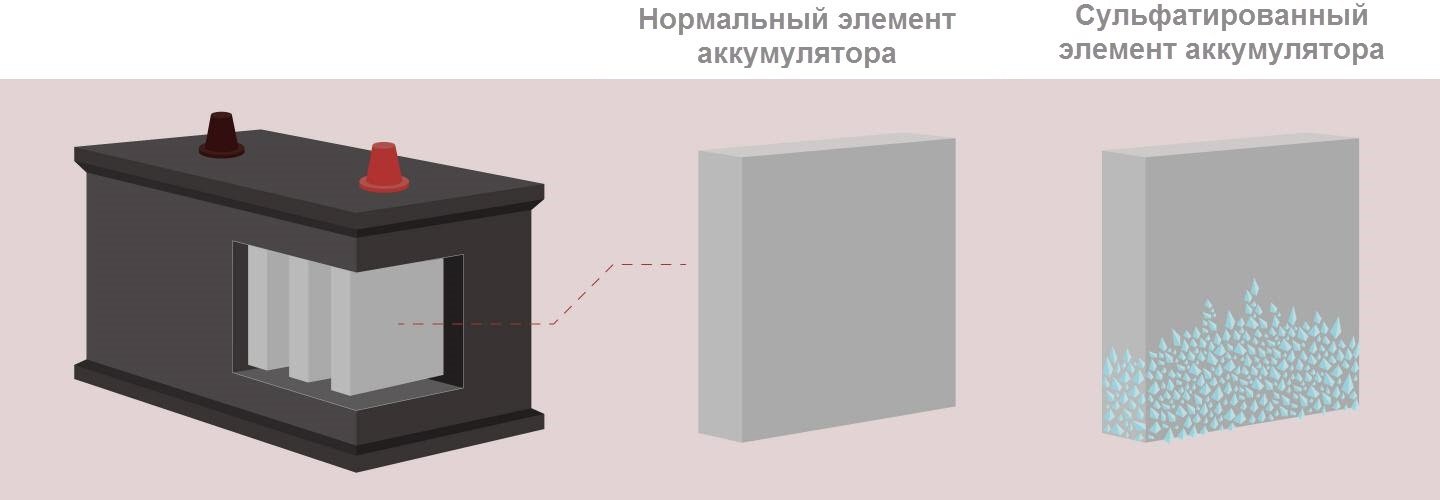
Sulfation refers to processes leading to the coating of battery plates with lead sulfate that occur during the discharge of a power source.
The electrolyte in the battery consists of two components: distilled water and sulfuric acid. During charging, water is consumed, and the plates cover lead (minus) and lead oxide (plus). In the reverse process (discharge), acid is already consumed, and the plates are coated with lead sulfate.
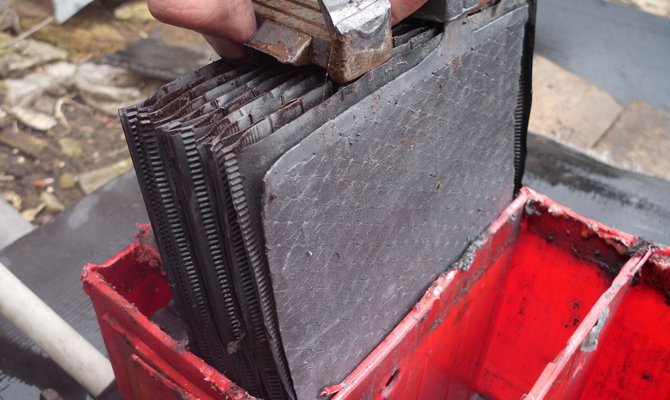
Lead sulfate on the plates of new batteries does not affect their performance in any way, because the natural cycles of discharging and recharging are accompanied by chemical reactions as a result of which small deposits of molecules form. However, in case of emergency situations, molecules are transformed into crystals, growing and sheathing plates, disrupting their normal functioning. This is due to a decrease in the working area of the element of the device, as a result of this leads to a decrease in battery capacity.
Small crystals that form with a slight discharge dissolve. Large crystals, appearing at zero charge, can no longer split and remain on the plates even at the maximum charge of the device.
Causes of Battery Sulfation
As already noted, many factors can cause battery sulphation. The main ones are as follows:
- Strong discharge. When the charge drops to the minimum mark, harmful processes are almost inevitable. The consequences become catastrophic after two or three strongest discharges.
- The cold season. It is worth noting that the battery is not afraid of frost as such. However, at sub-zero temperatures and a short duration of trips, the battery does not have time to heat up. This leads to the fact that the charging quality of the device is deteriorating, and much more energy is required for the vehicle engine plant in winter. These lead to plaque formation on the plates.
- Heat. Surprising that the heat is harmful to the car battery is not worth it. The engine compartment is limited and filled almost to the eyeballs with various units. In such conditions and in hot weather, the temperature around the battery rises to seventy degrees, which accelerates sulfation.
- Adding concentrated acid and an electrolyte “concentrate” to the electrolyte leads to the same consequences as exposure to high temperatures on the battery.
- Discharged storage. Since the plates are overgrown with crystals due to strong discharge, it is impossible to store a “planted” battery for a long period of time. Many motorists sin this and, putting the car in the parking lot, carry a dead battery home, where it costs more than six months.If, after twelve months, measure the battery charge, it will show less than forty percent of its original value.
How to eliminate sulfation
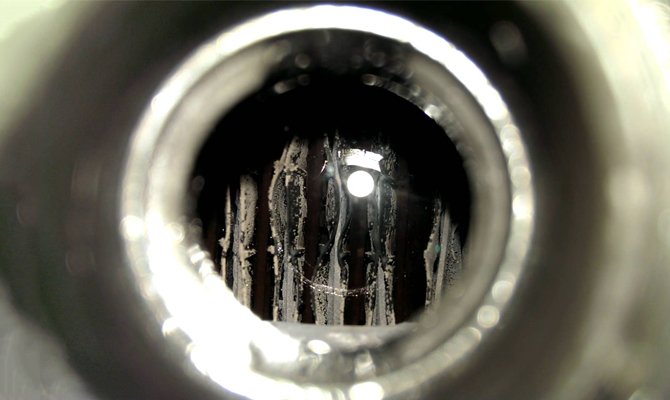
Elimination of sulfation is most effective if the owner of the car on time identified undesirable processes. How to do this? First you need to inspect the battery. If it has can lids, then it is serviced and you just need to turn them out to look inside. If there are deposits on the plates, the motorist will definitely notice them, because the contrast between pure bright gray lead and white crystals is striking.
In the event that the battery is maintenance-free, problems can be identified by indirect indications. The reduced functionality of the device, the strong boiling of the electrolyte and the fast discharge, indicates that measures must be taken. In addition, it is important to pay attention to capacity; it should not drop sharply.
The procedure for neutralizing sulfation is called desulfation. It can be carried out using both chemicals and current. The first method is not popular due to its complexity and the need to attract highly qualified specialists, but many people “treat” batteries with electric current.
The high amplitude of the pulsed current excites electrons on the surface of the plate. Lead sulfate deposits from such exposure are removed. To carry out such a procedure, a special device is necessary, which can be manufactured both in artisanal conditions and bought in a store. The cost of the latter is very high, which makes their purchase impractical, especially at the last station of battery sulfation.
Important! High-amplitude current can bring down the active mass of the battery, which will only reduce the capacity of the device.
A safer, but longer-lasting method of breaking down sulfation is to repeatedly charge the battery with low current. All that is required is a charger with the provided adjustments. The current is set at four hundredths of the base battery capacity. Charging is carried out for ten hours at a voltage of 14 volts. After a twelve-hour respite, the procedure is repeated at least three times. Each cycle increases the density and cleans the plates.
You can use an even more time-consuming method. First you need to charge the battery in the usual way, and then, after draining the electrolyte, pour distilled water into the jars and charge the device for two weeks. After that, the density of the electrolyte is checked. Due to the decomposition of plaque on the plates, distilled water is converted into an electrolyte with a low acid content. It again needs to be drained and the procedure will be repeated. Recovery can be considered a slight change in the density indicator after charging. The final step is to charge the battery with electrolyte and charge it under normal conditions.
How to reduce battery sulfation
In addition to desulfation, prevention is important in extending battery life. It allows you to reduce the intensity of undesirable processes and achieve normal battery use for seven years. Prevention includes the following actions:
- Battery storage should be carried out separately from the vehicle in a charged state;
- Tracking electrolyte levels;
- Charging the battery should be accompanied by control of the density of the electrolyte;
- The discharge and charge of the battery every six months.
A working battery is one of the main parts of a vehicle that allows it to be operated. Not only the motorist’s nerves, but also the size of his wallet depend on her condition.
Still have questions about plate sulphation or is there anything to add? Then write to us about it in the comments, this will make the material more useful, complete and accurate.